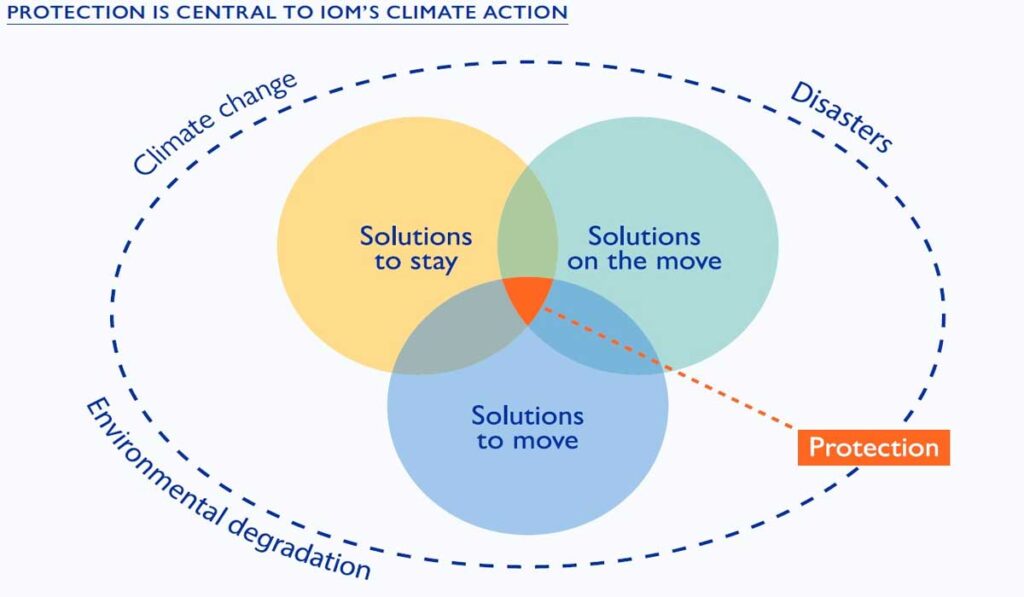
Environmental changes increasingly force communities to relocate, creating social, economic, and cultural challenges requiring solutions.
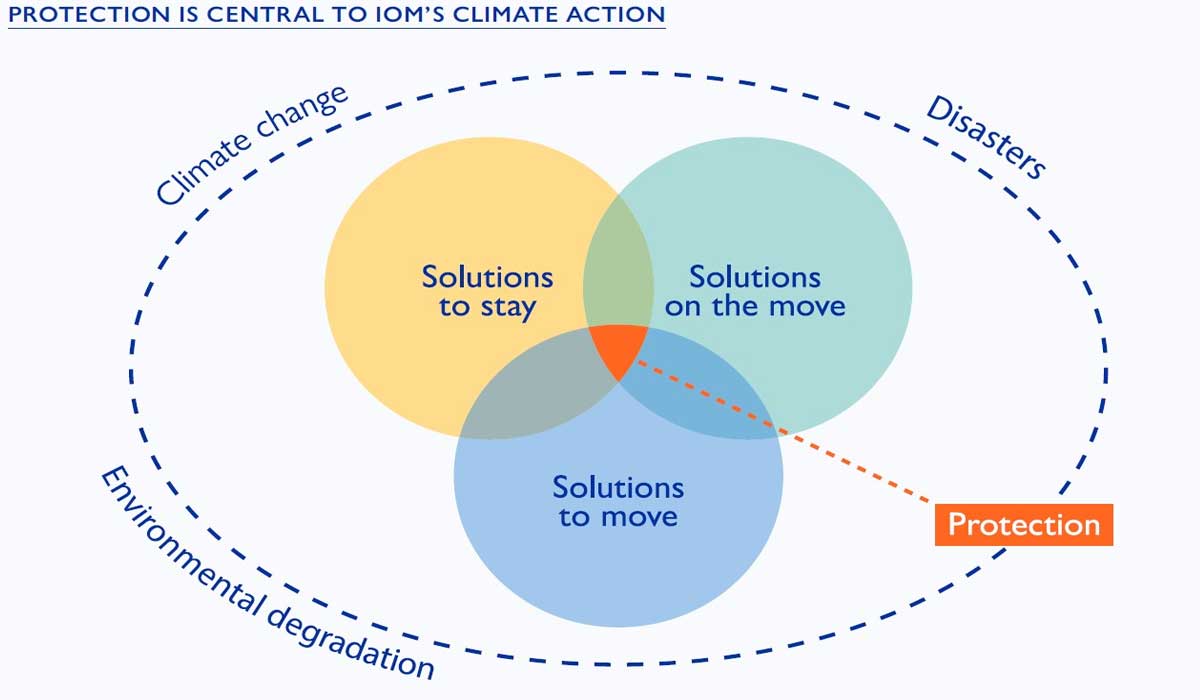
Rising sea levels, floods, droughts, and other ecological disasters threaten not only livelihoods but also social and economic stability. Bellow we, Web Hosting And Domain Names will understanding the causes, impacts, and possible solutions is essential to help displaced communities adapt and maintain their quality of life.
Major Drivers of Environmental Migration
Climate change is the primary driver of environmental migration. Extreme weather events such as floods, droughts, hurricanes, and coastal erosion destroy homes and livelihoods. Farmers lose fertile land, fishermen see their resources depleted, and coastal communities face frequent flooding, forcing them to relocate.
Human activities also exacerbate these issues. Deforestation, excessive urbanization, and pollution reduce the environment’s ability to sustain life. When natural resources decline and disaster risks increase, communities often have no choice but to seek safer areas.
Understanding these triggers helps governments and organizations anticipate migration patterns. Early identification of high-risk areas allows for better planning, preparedness, and support systems for vulnerable populations.
Social and Economic Impacts
Environmental migration carries significant social consequences. Communities face cultural integration challenges, family structure disruption, and psychological stress from losing homes and community identity. Children often lose access to education, while the elderly struggle to adjust to new surroundings.
Economically, traditional jobs such as farming and fishing may be unavailable in relocation areas. Many migrants turn to informal or temporary employment, increasing vulnerability to poverty and economic instability.
These combined effects underline the importance of holistic planning. Addressing both social and economic needs ensures migrants can rebuild stable, productive lives without losing community cohesion.
Challenges of Adaptation in New Locations
Relocated communities face integration challenges in new areas. Differences in language, culture, and local norms can hinder social interaction and access to support networks. Infrastructure like schools, healthcare, and transportation may also be insufficient.
Many migrants live in temporary or informal settlements, where safety, sanitation, and health services are limited. Without proper planning, these conditions can worsen vulnerabilities and lead to long-term disadvantages.
Addressing these challenges requires coordinated efforts between local authorities, NGOs, and community leaders. Providing adequate facilities and support programs is key to ensuring smooth adaptation.
Read Also: Apotek Professional Hosting And Domain For Pharmaceutical Business
Solutions for Affected Communities

Well-planned relocation programs are critical. Housing, access to education, and employment opportunities should accompany physical moves. Sustainable relocation strategies preserve community identity while enhancing long-term resilience.
Community-based adaptation programs are equally important. Skills training, eco-friendly infrastructure, and social network support help residents adjust while maintaining livelihoods. Such initiatives empower communities to respond proactively to environmental change.
By combining relocation and community-led adaptation, migrants can thrive in new locations while minimizing disruption to their lives and wellbeing.
Role of Governments and International Agencies
Governments play a crucial role in managing environmental migration. Policies on land use, disaster mitigation, and migrant protection ensure safety and reduce conflict. Effective governance guarantees that migrants access essential services in a timely manner.
International agencies complement local efforts with funding, research, and knowledge sharing. Global collaboration supports climate adaptation, sustainable development, and protection of environmental migrants’ rights.
Through coordinated efforts, both local and international actors can provide comprehensive support to communities affected by environmental change, ensuring security, resilience, and long-term sustainability, keep watching only at Web Hosting And Domain Names.
Image Source:
- First Image environmentalmigration.iom.int
- Second Image yourdictionary.com